Viewing the Commit History
After you have created several commits, or if you have cloned a repository with an existing commit history, you’ll probably want to look back to see what has happened. The most basic and powerful tool to do this is the git log command.
These examples use a very simple project called simplegit that I often use for demonstrations. To get the project, run
git clone git://github.com/schacon/simplegit-progit.gitWhen you run git log in this project, you should get output that looks something like this:
$ git log
commit ca82a6dff817ec66f44342007202690a93763949
Author: Scott Chacon <schacon@gee-mail.com>
Date: Mon Mar 17 21:52:11 2008 -0700
changed the version number
commit 085bb3bcb608e1e8451d4b2432f8ecbe6306e7e7
Author: Scott Chacon <schacon@gee-mail.com>
Date: Sat Mar 15 16:40:33 2008 -0700
removed unnecessary test code
commit a11bef06a3f659402fe7563abf99ad00de2209e6
Author: Scott Chacon <schacon@gee-mail.com>
Date: Sat Mar 15 10:31:28 2008 -0700
first commitBy default, with no arguments, git log lists the commits made in that repository in reverse chronological order. That is, the most recent commits show up first. As you can see, this command lists each commit with its SHA-1 checksum, the author’s name and e-mail, the date written, and the commit message.
A huge number and variety of options to the git log command are available to show you exactly what you’re looking for. Here, we’ll show you some of the most-used options.
One of the more helpful options is -p, which shows the diff introduced in each commit. You can also use -2, which limits the output to only the last two entries:
$ git log -p -2
commit ca82a6dff817ec66f44342007202690a93763949
Author: Scott Chacon <schacon@gee-mail.com>
Date: Mon Mar 17 21:52:11 2008 -0700
changed the version number
diff --git a/Rakefile b/Rakefile
index a874b73..8f94139 100644
--- a/Rakefile
+++ b/Rakefile
@@ -5,5 +5,5 @@ require 'rake/gempackagetask'
spec = Gem::Specification.new do |s|
s.name = "simplegit"
- s.version = "0.1.0"
+ s.version = "0.1.1"
s.author = "Scott Chacon"
s.email = "schacon@gee-mail.com
commit 085bb3bcb608e1e8451d4b2432f8ecbe6306e7e7
Author: Scott Chacon <schacon@gee-mail.com>
Date: Sat Mar 15 16:40:33 2008 -0700
removed unnecessary test code
diff --git a/lib/simplegit.rb b/lib/simplegit.rb
index a0a60ae..47c6340 100644
--- a/lib/simplegit.rb
+++ b/lib/simplegit.rb
@@ -18,8 +18,3 @@ class SimpleGit
end
end
-
-if $0 == __FILE__
- git = SimpleGit.new
- puts git.show
-end
\ No newline at end of fileThis option displays the same information but with a diff directly following each entry. This is very helpful for code review or to quickly browse what happened during a series of commits that a collaborator has added.
Sometimes it's easier to review changes on the word level rather than on the line level. There is a --word-diff option available in Git, that you can append to the git log -p command to get word diff instead of normal line by line diff. Word diff format is quite useless when applied to source code, but it comes in handy when applied to large text files, like books or your dissertation. Here is an example:
$ git log -U1 --word-diff
commit ca82a6dff817ec66f44342007202690a93763949
Author: Scott Chacon <schacon@gee-mail.com>
Date: Mon Mar 17 21:52:11 2008 -0700
changed the version number
diff --git a/Rakefile b/Rakefile
index a874b73..8f94139 100644
--- a/Rakefile
+++ b/Rakefile
@@ -7,3 +7,3 @@ spec = Gem::Specification.new do |s|
s.name = "simplegit"
s.version = [-"0.1.0"-]{+"0.1.1"+}
s.author = "Scott Chacon"As you can see, there is no added and removed lines in this output as in a normal diff. Changes are shown inline instead. You can see the added word enclosed in {+ +} and removed one enclosed in [- -]. You may also want to reduce the usual three lines context in diff output to only one line, as the context is now words, not lines. You can do this with -U1 as we did in the example above.
You can also use a series of summarizing options with git log. For example, if you want to see some abbreviated stats for each commit, you can use the --stat option:
$ git log --stat
commit ca82a6dff817ec66f44342007202690a93763949
Author: Scott Chacon <schacon@gee-mail.com>
Date: Mon Mar 17 21:52:11 2008 -0700
changed the version number
Rakefile | 2 +-
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+), 1 deletion(-)
commit 085bb3bcb608e1e8451d4b2432f8ecbe6306e7e7
Author: Scott Chacon <schacon@gee-mail.com>
Date: Sat Mar 15 16:40:33 2008 -0700
removed unnecessary test code
lib/simplegit.rb | 5 -----
1 file changed, 5 deletions(-)
commit a11bef06a3f659402fe7563abf99ad00de2209e6
Author: Scott Chacon <schacon@gee-mail.com>
Date: Sat Mar 15 10:31:28 2008 -0700
first commit
README | 6 ++++++
Rakefile | 23 +++++++++++++++++++++++
lib/simplegit.rb | 25 +++++++++++++++++++++++++
3 files changed, 54 insertions(+)As you can see, the --stat option prints below each commit entry a list of modified files, how many files were changed, and how many lines in those files were added and removed. It also puts a summary of the information at the end.
Another really useful option is --pretty. This option changes the log output to formats other than the default. A few prebuilt options are available for you to use. The oneline option prints each commit on a single line, which is useful if you’re looking at a lot of commits. In addition, the short, full, and fuller options show the output in roughly the same format but with less or more information, respectively:
$ git log --pretty=oneline
ca82a6dff817ec66f44342007202690a93763949 changed the version number
085bb3bcb608e1e8451d4b2432f8ecbe6306e7e7 removed unnecessary test code
a11bef06a3f659402fe7563abf99ad00de2209e6 first commitThe most interesting option is format, which allows you to specify your own log output format. This is especially useful when you’re generating output for machine parsing — because you specify the format explicitly, you know it won’t change with updates to Git:
$ git log --pretty=format:"%h - %an, %ar : %s"
ca82a6d - Scott Chacon, 11 months ago : changed the version number
085bb3b - Scott Chacon, 11 months ago : removed unnecessary test code
a11bef0 - Scott Chacon, 11 months ago : first commitTable 2-1 lists some of the more useful options that format takes.
<!-- Attention to translators: this is a table declaration. The lines must be formatted as follows <TAB><First column text><TAB><Second column text> -->
Option Description of Output
%H Commit hash
%h Abbreviated commit hash
%T Tree hash
%t Abbreviated tree hash
%P Parent hashes
%p Abbreviated parent hashes
%an Author name
%ae Author e-mail
%ad Author date (format respects the --date= option)
%ar Author date, relative
%cn Committer name
%ce Committer email
%cd Committer date
%cr Committer date, relative
%s SubjectYou may be wondering what the difference is between author and committer. The author is the person who originally wrote the patch, whereas the committer is the person who last applied the patch. So, if you send in a patch to a project and one of the core members applies the patch, both of you get credit — you as the author and the core member as the committer. We’ll cover this distinction a bit more in Chapter 5.
The oneline and format options are particularly useful with another log option called --graph. This option adds a nice little ASCII graph showing your branch and merge history, which we can see in our copy of the Grit project repository:
$ git log --pretty=format:"%h %s" --graph
* 2d3acf9 ignore errors from SIGCHLD on trap
* 5e3ee11 Merge branch 'master' of git://github.com/dustin/grit
|\
| * 420eac9 Added a method for getting the current branch.
* | 30e367c timeout code and tests
* | 5a09431 add timeout protection to grit
* | e1193f8 support for heads with slashes in them
|/
* d6016bc require time for xmlschema
* 11d191e Merge branch 'defunkt' into localThose are only some simple output-formatting options to git log — there are many more. Table 2-2 lists the options we’ve covered so far and some other common formatting options that may be useful, along with how they change the output of the log command.
<!-- Attention to translators: this is a table declaration. The lines must be formatted as follows <TAB><First column text><TAB><Second column text> -->
Option Description
-p Show the patch introduced with each commit.
--word-diff Show the patch in a word diff format.
--stat Show statistics for files modified in each commit.
--shortstat Display only the changed/insertions/deletions line from the --stat command.
--name-only Show the list of files modified after the commit information.
--name-status Show the list of files affected with added/modified/deleted information as well.
--abbrev-commit Show only the first few characters of the SHA-1 checksum instead of all 40.
--relative-date Display the date in a relative format (for example, “2 weeks ago”) instead of using the full date format.
--graph Display an ASCII graph of the branch and merge history beside the log output.
--pretty Show commits in an alternate format. Options include oneline, short, full, fuller, and format (where you specify your own format).
--oneline A convenience option short for `--pretty=oneline --abbrev-commit`.Limiting Log Output
In addition to output-formatting options, git log takes a number of useful limiting options — that is, options that let you show only a subset of commits. You’ve seen one such option already — the -2 option, which shows only the last two commits. In fact, you can do -<n>, where n is any integer to show the last n commits. In reality, you’re unlikely to use that often, because Git by default pipes all output through a pager so you see only one page of log output at a time.
However, the time-limiting options such as --since and --until are very useful. For example, this command gets the list of commits made in the last two weeks:
$ git log --since=2.weeksThis command works with lots of formats — you can specify a specific date (“2008-01-15”) or a relative date such as “2 years 1 day 3 minutes ago”.
You can also filter the list to commits that match some search criteria. The --author option allows you to filter on a specific author, and the --grep option lets you search for keywords in the commit messages. (Note that if you specify both author and grep options, the command will match commits with both.)
If you want to specify multiple grep options, you have to add --all-match or the command will match commits with either.
The last really useful option to pass to git log as a filter is a path. If you specify a directory or file name, you can limit the log output to commits that introduced a change to those files. This is always the last option and is generally preceded by double dashes (--) to separate the paths from the options.
In Table 2-3 we’ll list these and a few other common options for your reference.
<!-- Attention to translators: this is a table declaration. The lines must be formatted as follows <TAB><First column text><TAB><Second column text> -->
Option Description
-(n) Show only the last n commits
--since, --after Limit the commits to those whose CommitDate was made on-or-after the specified date/time.
--until, --before Limit the commits to those whose CommitDate was made on-or-before the specified date/time.
--author Only show commits in which the author entry matches the specified string.
--committer Only show commits in which the committer entry matches the specified string.Limiting Log Output according to Date/Time
To determine which commits in the Git source code repository (git://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/git/git.git) have CommitDate on 2014-04-29 relative to your local timezone (as set on your computer), use
$ git log --after="2014-04-29 00:00:00" --before="2014-04-29 23:59:59" \
--pretty=fullerAs the output will be different according to the timezone where it will be run, it's recommended to always use an absolute time such as ISO 8601 format (which includes timezone information) as argument to --after and --before, so that everone running the command will get the same repeatable results.
To obtain commits made at a specific instant in time (e.g. 29 April 2013 at 17:07:22 CET), we can use
$ git log --after="2013-04-29T17:07:22+0200" \
--before="2013-04-29T17:07:22+0200" --pretty=fuller
commit de7c201a10857e5d424dbd8db880a6f24ba250f9
Author: Ramkumar Ramachandra <artagnon@gmail.com>
AuthorDate: Mon Apr 29 18:19:37 2013 +0530
Commit: Junio C Hamano <gitster@pobox.com>
CommitDate: Mon Apr 29 08:07:22 2013 -0700
git-completion.bash: lexical sorting for diff.statGraphWidth
df44483a (diff --stat: add config option to limit graph width,
2012-03-01) added the option diff.startGraphWidth to the list of
configuration variables in git-completion.bash, but failed to notice
that the list is sorted alphabetically. Move it to its rightful place
in the list.
Signed-off-by: Ramkumar Ramachandra <artagnon@gmail.com>
Signed-off-by: Junio C Hamano <gitster@pobox.com>The above times (AuthorDate, CommitDate) are displayed in default format (--date=default), which shows timezone information of respective author and commiter.
Other useful formats include --date=iso (ISO 8601), --date=rfc (RFC 2822), --date=raw (seconds since the epoch (1970-01-01 UTC)) --date=local (times according to your local timezone) as well as --date=relative (e.g. "2 hours ago").
When using git log without specifying time, the time defaults to the time at which the command is run on your computer (keeping the identical offset from UTC).
For example, running a git log at 09:00 on your computer with your timezone currently 3 hours ahead of UTC, makes the following two commands equivalent:
$ git log --after=2008-06-01 --before=2008-07-01
$ git log --after="2008-06-01T09:00:00+0300" \
--before="2008-07-01T09:00:00+0300"As a final example, if you want to see which commits modifying test files in the Git source code history were committed by Junio Hamano with CommitDate being in the month of October 2008 (relative to the timezone of New York) and were not merges, you can run something like this:
$ git log --pretty="%h - %s" --author=gitster \
--after="2008-10-01T00:00:00-0400" \
--before="2008-10-31T23:59:59-0400" --no-merges -- t/
5610e3b - Fix testcase failure when extended attribute
acd3b9e - Enhance hold_lock_file_for_{update,append}()
f563754 - demonstrate breakage of detached checkout wi
d1a43f2 - reset --hard/read-tree --reset -u: remove un
51a94af - Fix "checkout --track -b newbranch" on detac
b0ad11e - pull: allow "git pull origin $something:$curOf the more than 36,000 commits in the Git source code history, this command shows the 6 that match those criteria.
Using a GUI to Visualize History
If you like to use a more graphical tool to visualize your commit history, you may want to take a look at a Tcl/Tk program called gitk that is distributed with Git. Gitk is basically a visual git log tool, and it accepts nearly all the filtering options that git log does. If you type gitk on the command line in your project, you should see something like Figure 2-2.
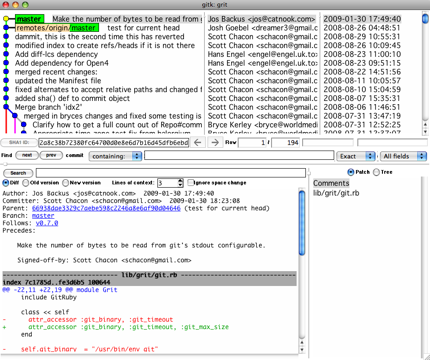 Figure 2-2. The gitk history visualizer.
Figure 2-2. The gitk history visualizer.
You can see the commit history in the top half of the window along with a nice ancestry graph. The diff viewer in the bottom half of the window shows you the changes introduced at any commit you click.
