Contributing to a Project
You know what the different workflows are, and you should have a pretty good grasp of fundamental Git usage. In this section, you’ll learn about a few common patterns for contributing to a project.
The main difficulty with describing this process is that there are a huge number of variations on how it’s done. Because Git is very flexible, people can and do work together many ways, and it’s problematic to describe how you should contribute to a project — every project is a bit different. Some of the variables involved are active contributor size, chosen workflow, your commit access, and possibly the external contribution method.
The first variable is active contributor size. How many users are actively contributing code to this project, and how often? In many instances, you’ll have two or three developers with a few commits a day, or possibly less for somewhat dormant projects. For really large companies or projects, the number of developers could be in the thousands, with dozens or even hundreds of patches coming in each day. This is important because with more and more developers, you run into more issues with making sure your code applies cleanly or can be easily merged. Changes you submit may be rendered obsolete or severely broken by work that is merged in while you were working or while your changes were waiting to be approved or applied. How can you keep your code consistently up to date and your patches valid?
The next variable is the workflow in use for the project. Is it centralized, with each developer having equal write access to the main codeline? Does the project have a maintainer or integration manager who checks all the patches? Are all the patches peer-reviewed and approved? Are you involved in that process? Is a lieutenant system in place, and do you have to submit your work to them first?
The next issue is your commit access. The workflow required in order to contribute to a project is much different if you have write access to the project than if you don’t. If you don’t have write access, how does the project prefer to accept contributed work? Does it even have a policy? How much work are you contributing at a time? How often do you contribute?
All these questions can affect how you contribute effectively to a project and what workflows are preferred or available to you. I’ll cover aspects of each of these in a series of use cases, moving from simple to more complex; you should be able to construct the specific workflows you need in practice from these examples.
Commit Guidelines
Before you start looking at the specific use cases, here’s a quick note about commit messages. Having a good guideline for creating commits and sticking to it makes working with Git and collaborating with others a lot easier. The Git project provides a document that lays out a number of good tips for creating commits from which to submit patches — you can read it in the Git source code in the Documentation/SubmittingPatches file.
First, you don’t want to submit any whitespace errors. Git provides an easy way to check for this — before you commit, run git diff --check, which identifies possible whitespace errors and lists them for you. Here is an example, where I’ve replaced a red terminal color with Xs:
$ git diff --check
lib/simplegit.rb:5: trailing whitespace.
+ @git_dir = File.expand_path(git_dir)XX
lib/simplegit.rb:7: trailing whitespace.
+ XXXXXXXXXXX
lib/simplegit.rb:26: trailing whitespace.
+ def command(git_cmd)XXXXIf you run that command before committing, you can tell if you’re about to commit whitespace issues that may annoy other developers.
Next, try to make each commit a logically separate changeset. If you can, try to make your changes digestible — don’t code for a whole weekend on five different issues and then submit them all as one massive commit on Monday. Even if you don’t commit during the weekend, use the staging area on Monday to split your work into at least one commit per issue, with a useful message per commit. If some of the changes modify the same file, try to use git add --patch to partially stage files (covered in detail in Chapter 6). The project snapshot at the tip of the branch is identical whether you do one commit or five, as long as all the changes are added at some point, so try to make things easier on your fellow developers when they have to review your changes. This approach also makes it easier to pull out or revert one of the changesets if you need to later. Chapter 6 describes a number of useful Git tricks for rewriting history and interactively staging files — use these tools to help craft a clean and understandable history.
The last thing to keep in mind is the commit message. Getting in the habit of creating quality commit messages makes using and collaborating with Git a lot easier. As a general rule, your messages should start with a single line that’s no more than about 50 characters and that describes the changeset concisely, followed by a blank line, followed by a more detailed explanation. The Git project requires that the more detailed explanation include your motivation for the change and contrast its implementation with previous behavior — this is a good guideline to follow. It’s also a good idea to use the imperative present tense in these messages. In other words, use commands. Instead of "I added tests for" or "Adding tests for," use "Add tests for." Here is a template originally written by Tim Pope at tpope.net:
Short (50 chars or less) summary of changes
More detailed explanatory text, if necessary. Wrap it to about 72
characters or so. In some contexts, the first line is treated as the
subject of an email and the rest of the text as the body. The blank
line separating the summary from the body is critical (unless you omit
the body entirely); tools like rebase can get confused if you run the
two together.
Further paragraphs come after blank lines.
- Bullet points are okay, too
- Typically a hyphen or asterisk is used for the bullet, preceded by a
single space, with blank lines in between, but conventions vary hereIf all your commit messages look like this, things will be a lot easier for you and the developers you work with. The Git project has well-formatted commit messages — I encourage you to run git log --no-merges there to see what a nicely formatted project-commit history looks like.
In the following examples, and throughout most of this book, for the sake of brevity I don’t format messages nicely like this; instead, I use the -m option to git commit. Do as I say, not as I do.
Private Small Team
The simplest setup you’re likely to encounter is a private project with one or two other developers. By private, I mean closed source — not read-accessible to the outside world. You and the other developers all have push access to the repository.
In this environment, you can follow a workflow similar to what you might do when using Subversion or another centralized system. You still get the advantages of things like offline committing and vastly simpler branching and merging, but the workflow can be very similar; the main difference is that merges happen client-side rather than on the server at commit time.
Let’s see what it might look like when two developers start to work together with a shared repository. The first developer, John, clones the repository, makes a change, and commits locally. (I’m replacing the protocol messages with ... in these examples to shorten them somewhat.)
# John's Machine
$ git clone john@githost:simplegit.git
Initialized empty Git repository in /home/john/simplegit/.git/
...
$ cd simplegit/
$ vim lib/simplegit.rb
$ git commit -am 'removed invalid default value'
[master 738ee87] removed invalid default value
1 files changed, 1 insertions(+), 1 deletions(-)The second developer, Jessica, does the same thing — clones the repository and commits a change:
# Jessica's Machine
$ git clone jessica@githost:simplegit.git
Initialized empty Git repository in /home/jessica/simplegit/.git/
...
$ cd simplegit/
$ vim TODO
$ git commit -am 'add reset task'
[master fbff5bc] add reset task
1 files changed, 1 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-)Now, Jessica pushes her work up to the server:
# Jessica's Machine
$ git push origin master
...
To jessica@githost:simplegit.git
1edee6b..fbff5bc master -> masterJohn tries to push his change up, too:
# John's Machine
$ git push origin master
To john@githost:simplegit.git
! [rejected] master -> master (non-fast forward)
error: failed to push some refs to 'john@githost:simplegit.git'John isn’t allowed to push because Jessica has pushed in the meantime. This is especially important to understand if you’re used to Subversion, because you’ll notice that the two developers didn’t edit the same file. Although Subversion automatically does such a merge on the server if different files are edited, in Git you must merge the commits locally. John has to fetch Jessica’s changes and merge them in before he will be allowed to push:
$ git fetch origin
...
From john@githost:simplegit
+ 049d078...fbff5bc master -> origin/masterAt this point, John’s local repository looks something like Figure 5-4.
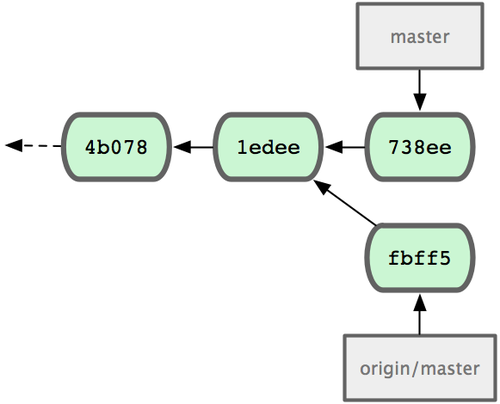 Figure 5-4. John’s initial repository.
Figure 5-4. John’s initial repository.
John has a reference to the changes Jessica pushed up, but he has to merge them into his own work before he is allowed to push:
$ git merge origin/master
Merge made by recursive.
TODO | 1 +
1 files changed, 1 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-)The merge goes smoothly — John’s commit history now looks like Figure 5-5.
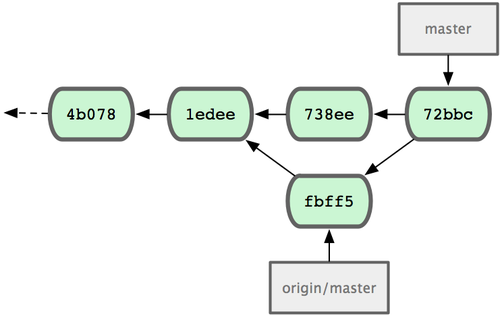 Figure 5-5. John’s repository after merging
Figure 5-5. John’s repository after merging origin/master.
Now, John can test his code to make sure it still works properly, and then he can push his new merged work up to the server:
$ git push origin master
...
To john@githost:simplegit.git
fbff5bc..72bbc59 master -> masterFinally, John’s commit history looks like Figure 5-6.
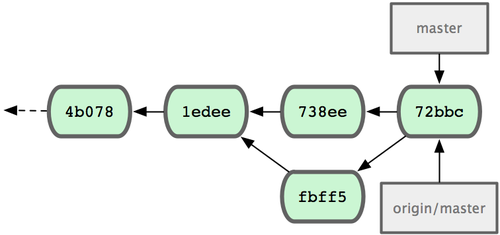 Figure 5-6. John’s history after pushing to the origin server.
Figure 5-6. John’s history after pushing to the origin server.
In the meantime, Jessica has been working on a topic branch. She’s created a topic branch called issue54 and done three commits on that branch. She hasn’t fetched John’s changes yet, so her commit history looks like Figure 5-7.
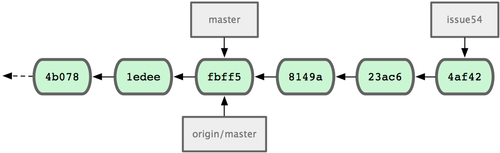 Figure 5-7. Jessica’s initial commit history.
Figure 5-7. Jessica’s initial commit history.
Jessica wants to sync up with John, so she fetches:
# Jessica's Machine
$ git fetch origin
...
From jessica@githost:simplegit
fbff5bc..72bbc59 master -> origin/masterThat pulls down the work John has pushed up in the meantime. Jessica’s history now looks like Figure 5-8.
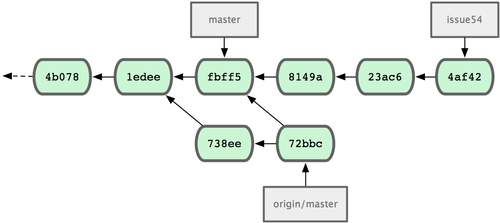 Figure 5-8. Jessica’s history after fetching John’s changes.
Figure 5-8. Jessica’s history after fetching John’s changes.
Jessica thinks her topic branch is ready, but she wants to know what she has to merge her work into so that she can push. She runs git log to find out:
$ git log --no-merges origin/master ^issue54
commit 738ee872852dfaa9d6634e0dea7a324040193016
Author: John Smith <jsmith@example.com>
Date: Fri May 29 16:01:27 2009 -0700
removed invalid default valueNow, Jessica can merge her topic work into her master branch, merge John’s work (origin/master) into her master branch, and then push back to the server again. First, she switches back to her master branch to integrate all this work:
$ git checkout master
Switched to branch "master"
Your branch is behind 'origin/master' by 2 commits, and can be fast-forwarded.She can merge either origin/master or issue54 first — they’re both upstream, so the order doesn’t matter. The end snapshot should be identical no matter which order she chooses; only the history will be slightly different. She chooses to merge in issue54 first:
$ git merge issue54
Updating fbff5bc..4af4298
Fast forward
README | 1 +
lib/simplegit.rb | 6 +++++-
2 files changed, 6 insertions(+), 1 deletions(-)No problems occur; as you can see, it was a simple fast-forward. Now Jessica merges in John’s work (origin/master):
$ git merge origin/master
Auto-merging lib/simplegit.rb
Merge made by recursive.
lib/simplegit.rb | 2 +-
1 files changed, 1 insertions(+), 1 deletions(-)Everything merges cleanly, and Jessica’s history looks like Figure 5-9.
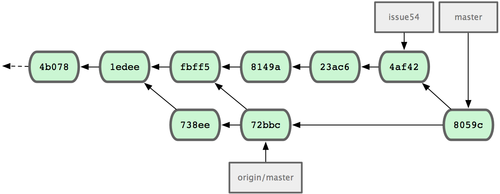 Figure 5-9. Jessica’s history after merging John’s changes.
Figure 5-9. Jessica’s history after merging John’s changes.
Now origin/master is reachable from Jessica’s master branch, so she should be able to successfully push (assuming John hasn’t pushed again in the meantime):
$ git push origin master
...
To jessica@githost:simplegit.git
72bbc59..8059c15 master -> masterEach developer has committed a few times and merged each other’s work successfully; see Figure 5-10.
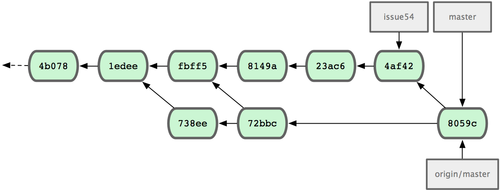 Figure 5-10. Jessica’s history after pushing all changes back to the server.
Figure 5-10. Jessica’s history after pushing all changes back to the server.
That is one of the simplest workflows. You work for a while, generally in a topic branch, and merge into your master branch when it’s ready to be integrated. When you want to share that work, you merge it into your own master branch, then fetch and merge origin/master if it has changed, and finally push to the master branch on the server. The general sequence is something like that shown in Figure 5-11.
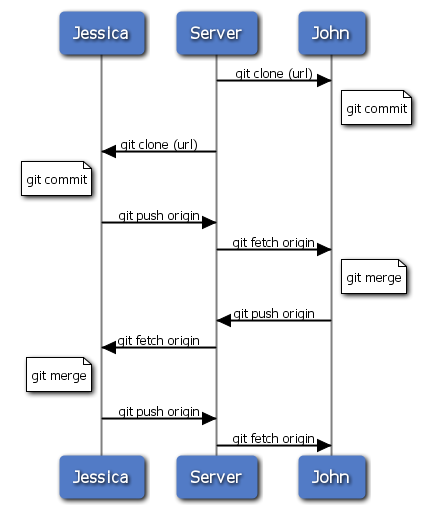 Figure 5-11. General sequence of events for a simple multiple-developer Git workflow.
Figure 5-11. General sequence of events for a simple multiple-developer Git workflow.
Private Managed Team
In this next scenario, you’ll look at contributor roles in a larger private group. You’ll learn how to work in an environment where small groups collaborate on features and then those team-based contributions are integrated by another party.
Let’s say that John and Jessica are working together on one feature, while Jessica and Josie are working on a second. In this case, the company is using a type of integration-manager workflow where the work of the individual groups is integrated only by certain engineers, and the master branch of the main repo can be updated only by those engineers. In this scenario, all work is done in team-based branches and pulled together by the integrators later.
Let’s follow Jessica’s workflow as she works on her two features, collaborating in parallel with two different developers in this environment. Assuming she already has her repository cloned, she decides to work on featureA first. She creates a new branch for the feature and does some work on it there:
# Jessica's Machine
$ git checkout -b featureA
Switched to a new branch "featureA"
$ vim lib/simplegit.rb
$ git commit -am 'add limit to log function'
[featureA 3300904] add limit to log function
1 files changed, 1 insertions(+), 1 deletions(-)At this point, she needs to share her work with John, so she pushes her featureA branch commits up to the server. Jessica doesn’t have push access to the master branch — only the integrators do — so she has to push to another branch in order to collaborate with John:
$ git push origin featureA
...
To jessica@githost:simplegit.git
* [new branch] featureA -> featureAJessica e-mails John to tell him that she’s pushed some work into a branch named featureA and he can look at it now. While she waits for feedback from John, Jessica decides to start working on featureB with Josie. To begin, she starts a new feature branch, basing it off the server’s master branch:
# Jessica's Machine
$ git fetch origin
$ git checkout -b featureB origin/master
Switched to a new branch "featureB"Now, Jessica makes a couple of commits on the featureB branch:
$ vim lib/simplegit.rb
$ git commit -am 'made the ls-tree function recursive'
[featureB e5b0fdc] made the ls-tree function recursive
1 files changed, 1 insertions(+), 1 deletions(-)
$ vim lib/simplegit.rb
$ git commit -am 'add ls-files'
[featureB 8512791] add ls-files
1 files changed, 5 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-)Jessica’s repository looks like Figure 5-12.
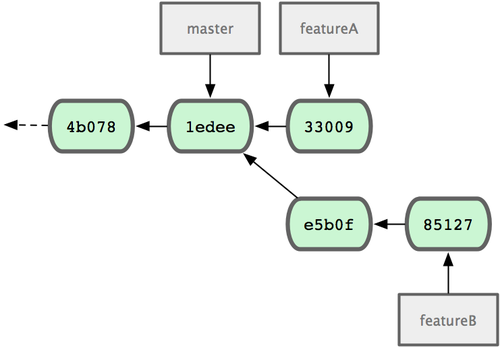 Figure 5-12. Jessica’s initial commit history.
Figure 5-12. Jessica’s initial commit history.
She’s ready to push up her work, but gets an e-mail from Josie that a branch with some initial work on it was already pushed to the server as featureBee. Jessica first needs to merge those changes in with her own before she can push to the server. She can then fetch Josie’s changes down with git fetch:
$ git fetch origin
...
From jessica@githost:simplegit
* [new branch] featureBee -> origin/featureBeeJessica can now merge this into the work she did with git merge:
$ git merge origin/featureBee
Auto-merging lib/simplegit.rb
Merge made by recursive.
lib/simplegit.rb | 4 ++++
1 files changed, 4 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-)There is a bit of a problem — she needs to push the merged work in her featureB branch to the featureBee branch on the server. She can do so by specifying the local branch followed by a colon (:) followed by the remote branch to the git push command:
$ git push origin featureB:featureBee
...
To jessica@githost:simplegit.git
fba9af8..cd685d1 featureB -> featureBeeThis is called a refspec. See Chapter 9 for a more detailed discussion of Git refspecs and different things you can do with them.
Next, John e-mails Jessica to say he’s pushed some changes to the featureA branch and ask her to verify them. She runs a git fetch to pull down those changes:
$ git fetch origin
...
From jessica@githost:simplegit
3300904..aad881d featureA -> origin/featureAThen, she can see what has been changed with git log:
$ git log origin/featureA ^featureA
commit aad881d154acdaeb2b6b18ea0e827ed8a6d671e6
Author: John Smith <jsmith@example.com>
Date: Fri May 29 19:57:33 2009 -0700
changed log output to 30 from 25Finally, she merges John’s work into her own featureA branch:
$ git checkout featureA
Switched to branch "featureA"
$ git merge origin/featureA
Updating 3300904..aad881d
Fast forward
lib/simplegit.rb | 10 +++++++++-
1 files changed, 9 insertions(+), 1 deletions(-)Jessica wants to tweak something, so she commits again and then pushes this back up to the server:
$ git commit -am 'small tweak'
[featureA 774b3ed] small tweak
1 files changed, 1 insertions(+), 1 deletions(-)
$ git push origin featureA
...
To jessica@githost:simplegit.git
3300904..774b3ed featureA -> featureAJessica’s commit history now looks something like Figure 5-13.
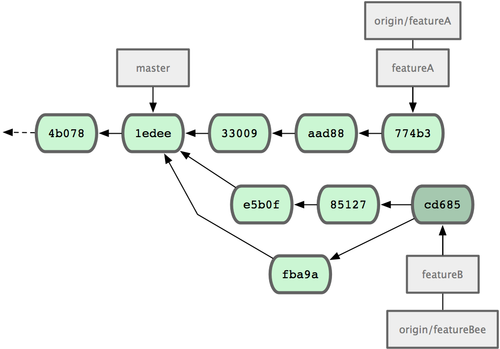 Figure 5-13. Jessica’s history after committing on a feature branch.
Figure 5-13. Jessica’s history after committing on a feature branch.
Jessica, Josie, and John inform the integrators that the featureA and featureBee branches on the server are ready for integration into the mainline. After they integrate these branches into the mainline, a fetch will bring down the new merge commits, making the commit history look like Figure 5-14.
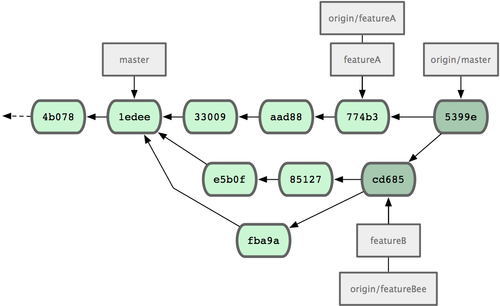 Figure 5-14. Jessica’s history after merging both her topic branches.
Figure 5-14. Jessica’s history after merging both her topic branches.
Many groups switch to Git because of this ability to have multiple teams working in parallel, merging the different lines of work late in the process. The ability of smaller subgroups of a team to collaborate via remote branches without necessarily having to involve or impede the entire team is a huge benefit of Git. The sequence for the workflow you saw here is something like Figure 5-15.
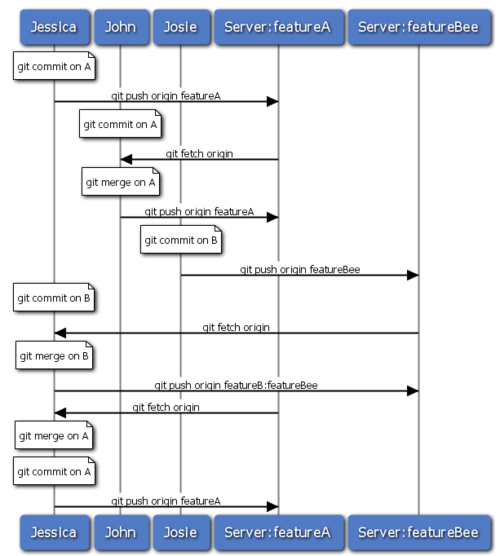 Figure 5-15. Basic sequence of this managed-team workflow.
Figure 5-15. Basic sequence of this managed-team workflow.
Public Small Project
Contributing to public projects is a bit different. Because you don’t have the permissions to directly update branches on the project, you have to get the work to the maintainers some other way. This first example describes contributing via forking on Git hosts that support easy forking. The repo.or.cz and GitHub hosting sites both support this, and many project maintainers expect this style of contribution. The next section deals with projects that prefer to accept contributed patches via e-mail.
First, you’ll probably want to clone the main repository, create a topic branch for the patch or patch series you’re planning to contribute, and do your work there. The sequence looks basically like this:
$ git clone (url)
$ cd project
$ git checkout -b featureA
$ (work)
$ git commit
$ (work)
$ git commitYou may want to use rebase -i to squash your work down to a single commit, or rearrange the work in the commits to make the patch easier for the maintainer to review — see Chapter 6 for more information about interactive rebasing.
When your branch work is finished and you’re ready to contribute it back to the maintainers, go to the original project page and click the "Fork" button, creating your own writable fork of the project. You then need to add in this new repository URL as a second remote, in this case named myfork:
$ git remote add myfork (url)You need to push your work up to it. It’s easiest to push the remote branch you’re working on up to your repository, rather than merging into your master branch and pushing that up. The reason is that if the work isn’t accepted or is cherry picked, you don’t have to rewind your master branch. If the maintainers merge, rebase, or cherry-pick your work, you’ll eventually get it back via pulling from their repository anyhow:
$ git push myfork featureAWhen your work has been pushed up to your fork, you need to notify the maintainer. This is often called a pull request, and you can either generate it via the website — GitHub has a "pull request" button that automatically messages the maintainer — or run the git request-pull command and e-mail the output to the project maintainer manually.
The request-pull command takes the base branch into which you want your topic branch pulled and the Git repository URL you want them to pull from, and outputs a summary of all the changes you’re asking to be pulled in. For instance, if Jessica wants to send John a pull request, and she’s done two commits on the topic branch she just pushed up, she can run this:
$ git request-pull origin/master myfork
The following changes since commit 1edee6b1d61823a2de3b09c160d7080b8d1b3a40:
John Smith (1):
added a new function
are available in the git repository at:
git://githost/simplegit.git featureA
Jessica Smith (2):
add limit to log function
change log output to 30 from 25
lib/simplegit.rb | 10 +++++++++-
1 files changed, 9 insertions(+), 1 deletions(-)The output can be sent to the maintainer—it tells them where the work was branched from, summarizes the commits, and tells where to pull this work from.
On a project for which you’re not the maintainer, it’s generally easier to have a branch like master always track origin/master and to do your work in topic branches that you can easily discard if they’re rejected. Having work themes isolated into topic branches also makes it easier for you to rebase your work if the tip of the main repository has moved in the meantime and your commits no longer apply cleanly. For example, if you want to submit a second topic of work to the project, don’t continue working on the topic branch you just pushed up — start over from the main repository’s master branch:
$ git checkout -b featureB origin/master
$ (work)
$ git commit
$ git push myfork featureB
$ (email maintainer)
$ git fetch originNow, each of your topics is contained within a silo — similar to a patch queue — that you can rewrite, rebase, and modify without the topics interfering or interdepending on each other as in Figure 5-16.
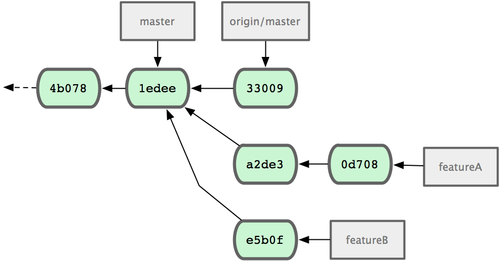 Figure 5-16. Initial commit history with featureB work.
Figure 5-16. Initial commit history with featureB work.
Let’s say the project maintainer has pulled in a bunch of other patches and tried your first branch, but it no longer cleanly merges. In this case, you can try to rebase that branch on top of origin/master, resolve the conflicts for the maintainer, and then resubmit your changes:
$ git checkout featureA
$ git rebase origin/master
$ git push -f myfork featureAThis rewrites your history to now look like Figure 5-17.
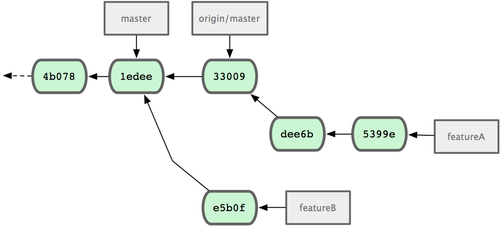 Figure 5-17. Commit history after featureA work.
Figure 5-17. Commit history after featureA work.
Because you rebased the branch, you have to specify the -f to your push command in order to be able to replace the featureA branch on the server with a commit that isn’t a descendant of it. An alternative would be to push this new work to a different branch on the server (perhaps called featureAv2).
Let’s look at one more possible scenario: the maintainer has looked at work in your second branch and likes the concept but would like you to change an implementation detail. You’ll also take this opportunity to move the work to be based off the project’s current master branch. You start a new branch based off the current origin/master branch, squash the featureB changes there, resolve any conflicts, make the implementation change, and then push that up as a new branch:
$ git checkout -b featureBv2 origin/master
$ git merge --no-commit --squash featureB
$ (change implementation)
$ git commit
$ git push myfork featureBv2The --squash option takes all the work on the merged branch and squashes it into one non-merge commit on top of the branch you’re on. The --no-commit option tells Git not to automatically record a commit. This allows you to introduce all the changes from another branch and then make more changes before recording the new commit.
Now you can send the maintainer a message that you’ve made the requested changes and they can find those changes in your featureBv2 branch (see Figure 5-18).
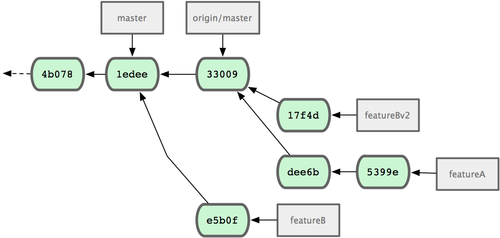 Figure 5-18. Commit history after featureBv2 work.
Figure 5-18. Commit history after featureBv2 work.
Public Large Project
Many larger projects have established procedures for accepting patches — you’ll need to check the specific rules for each project, because they will differ. However, many larger public projects accept patches via a developer mailing list, so I’ll go over an example of that now.
The workflow is similar to the previous use case — you create topic branches for each patch series you work on. The difference is how you submit them to the project. Instead of forking the project and pushing to your own writable version, you generate e-mail versions of each commit series and e-mail them to the developer mailing list:
$ git checkout -b topicA
$ (work)
$ git commit
$ (work)
$ git commitNow you have two commits that you want to send to the mailing list. You use git format-patch to generate the mbox-formatted files that you can e-mail to the list — it turns each commit into an e-mail message with the first line of the commit message as the subject and the rest of the message plus the patch that the commit introduces as the body. The nice thing about this is that applying a patch from an e-mail generated with format-patch preserves all the commit information properly, as you’ll see more of in the next section when you apply these patches:
$ git format-patch -M origin/master
0001-add-limit-to-log-function.patch
0002-changed-log-output-to-30-from-25.patchThe format-patch command prints out the names of the patch files it creates. The -M switch tells Git to look for renames. The files end up looking like this:
$ cat 0001-add-limit-to-log-function.patch
From 330090432754092d704da8e76ca5c05c198e71a8 Mon Sep 17 00:00:00 2001
From: Jessica Smith <jessica@example.com>
Date: Sun, 6 Apr 2008 10:17:23 -0700
Subject: [PATCH 1/2] add limit to log function
Limit log functionality to the first 20
---
lib/simplegit.rb | 2 +-
1 files changed, 1 insertions(+), 1 deletions(-)
diff --git a/lib/simplegit.rb b/lib/simplegit.rb
index 76f47bc..f9815f1 100644
--- a/lib/simplegit.rb
+++ b/lib/simplegit.rb
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ class SimpleGit
end
def log(treeish = 'master')
- command("git log #{treeish}")
+ command("git log -n 20 #{treeish}")
end
def ls_tree(treeish = 'master')
--
1.6.2.rc1.20.g8c5b.dirtyYou can also edit these patch files to add more information for the e-mail list that you don’t want to show up in the commit message. If you add text between the --- line and the beginning of the patch (the lib/simplegit.rb line), then developers can read it; but applying the patch excludes it.
To e-mail this to a mailing list, you can either paste the file into your e-mail program or send it via a command-line program. Pasting the text often causes formatting issues, especially with "smarter" clients that don’t preserve newlines and other whitespace appropriately. Luckily, Git provides a tool to help you send properly formatted patches via IMAP, which may be easier for you. I’ll demonstrate how to send a patch via Gmail, which happens to be the e-mail agent I use; you can read detailed instructions for a number of mail programs at the end of the aforementioned Documentation/SubmittingPatches file in the Git source code.
First, you need to set up the imap section in your ~/.gitconfig file. You can set each value separately with a series of git config commands, or you can add them manually; but in the end, your config file should look something like this:
[imap]
folder = "[Gmail]/Drafts"
host = imaps://imap.gmail.com
user = user@gmail.com
pass = p4ssw0rd
port = 993
sslverify = falseIf your IMAP server doesn’t use SSL, the last two lines probably aren’t necessary, and the host value will be imap:// instead of imaps://.
When that is set up, you can use git imap-send to place the patch series in the Drafts folder of the specified IMAP server:
$ cat *.patch |git imap-send
Resolving imap.gmail.com... ok
Connecting to [74.125.142.109]:993... ok
Logging in...
sending 2 messages
100% (2/2) doneAt this point, you should be able to go to your Drafts folder, change the To field to the mailing list you’re sending the patch to, possibly CC the maintainer or person responsible for that section, and send it off.
You can also send the patches through an SMTP server. As before, you can set each value separately with a series of git config commands, or you can add them manually in the sendemail section in your ~/.gitconfig file:
[sendemail]
smtpencryption = tls
smtpserver = smtp.gmail.com
smtpuser = user@gmail.com
smtpserverport = 587After this is done, you can use git send-email to send your patches:
$ git send-email *.patch
0001-added-limit-to-log-function.patch
0002-changed-log-output-to-30-from-25.patch
Who should the emails appear to be from? [Jessica Smith <jessica@example.com>]
Emails will be sent from: Jessica Smith <jessica@example.com>
Who should the emails be sent to? jessica@example.com
Message-ID to be used as In-Reply-To for the first email? yThen, Git spits out a bunch of log information looking something like this for each patch you’re sending:
(mbox) Adding cc: Jessica Smith <jessica@example.com> from
\line 'From: Jessica Smith <jessica@example.com>'
OK. Log says:
Sendmail: /usr/sbin/sendmail -i jessica@example.com
From: Jessica Smith <jessica@example.com>
To: jessica@example.com
Subject: [PATCH 1/2] added limit to log function
Date: Sat, 30 May 2009 13:29:15 -0700
Message-Id: <1243715356-61726-1-git-send-email-jessica@example.com>
X-Mailer: git-send-email 1.6.2.rc1.20.g8c5b.dirty
In-Reply-To: <y>
References: <y>
Result: OKSummary
This section has covered a number of common workflows for dealing with several very different types of Git projects you’re likely to encounter and introduced a couple of new tools to help you manage this process. Next, you’ll see how to work the other side of the coin: maintaining a Git project. You’ll learn how to be a benevolent dictator or integration manager.
